Case Studies
We provide plant protection and plant nutrition products that help build healthy and sustainable food systems.
Disease Control in Apple Brown Spot
Apple brown spot is a foliar disease that seriously affects fruit yield and quality. Its occurrence and popularity are related to weather, tree vigor, and cultivation management.
Fungicide
Apple brown spot is a foliar disease that seriously affects fruit yield and quality. The pathogen is Marssonina mali (P.Henn.) Ito, which overwinters on the diseased leaves as hyphae or conidia discs. The spores are produced after the rain in the second year and spread by wind or rain. The incubation period is generally 6 to 12 days and can be as long as 45 days in dry years. It takes about 13 to 55 days from the onset of the disease to the shedding of the diseased leaves.
Its occurrence and popularity are related to weather, tree vigor, and cultivation management. Rainy weather is more conducive to the prevalence of the disease. In rainy summer, the disease often occurs early and heavily. The disease tends to be more serious in poor field management, low-lying terrain, poor drainage, closed canopies, and poor ventilation.
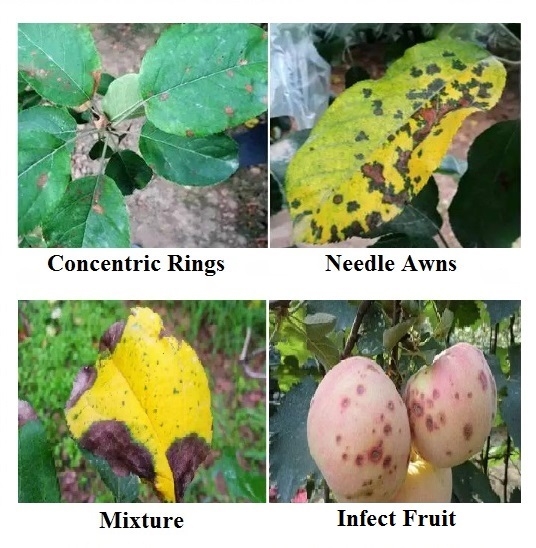
The lesions on the leaves are small brown spots at first and later develop into three different types of lesions: concentric rings, needle awns, and a mixture of concentric rings and needle awns, as shown in the figure. If the pathogen infects the fruit, the fruit surface first appears small pale brown spots, which gradually expand into dark brown

Sunjoy Recommendations
To prevent and control apple brown spot disease, it is important to strengthen overall field management, including reasonable pruning, timely removal of water accumulation in orchards and quickly cleaning of diseased leaves, branches, and fruits in autumn and winter. In addition, Sunjoy Agro recommends Synglo (Pyraclostrobin 160g/L + Tebuconazole 320g/L SC) with dilution rate of 3000-5000 times in fruit expansion stages.
Synglo has a protective and curative effect. Tebuconazole mainly inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol, which is a component of yeast and fungal cell membranes. Pyraclostrobin inhibits mitochondrial respiration by preventing electron transfer between cytochrome B and C1. It has the characteristics of permeability, long-lasting effect, and resistance to rain erosion. In addition, the product can promote crop growth and increase yield by improving plant vigor, enhancing root systems, and thickening leaves and stems.
Performance Results
1.Test purpose
The purpose of this study is to verify the control effect of Pyraclostrobin 160g/L + Tebuconazole 320g/L SC on apple brown spot.
2.Fungicide and Experiment
|
No. |
Fungicide |
Dilution factor |
|
A |
48% Pyraclostrobin • Tebuconazole SC |
3000 |
|
B |
48% Pyraclostrobin • Tebuconazole SC |
4000 |
|
C |
48% Pyraclostrobin • Tebuconazole SC |
5000 |
|
D |
75% Tebuconazole • Trifloxystrobin WG |
5000 |
|
E |
Untreatde |
|
3.Results
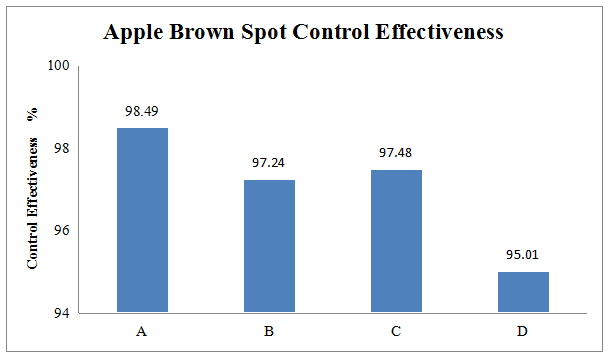
The test field is located in Yantai City, Shandong Province. The test variety is Red Fuji Apple. The trial period is from 6/28/2017 to 9/28/2017. The growth period is the fruit expansion stage and the apples have been bagged. Researchers applied the fungicide for the first time on 6/28 before brown spot disease occurred. Apply every 20 days on 6/28, 7/19, 8/11, and 9/22. A total of 4 sprays were applied until brown spot disease generally occurred in the untreated group. Control effectiveness was tested on 9/28.
Performance assessments are based upon results or analysis of Yantai Academy of Agricultural Sciences Institute of Plant Protection.
4.Conclusion
Under the conditions of this experiment, 48% Pyraclostrobin • Tebuconazole SC is safe for the tested apple varieties. It has a better control effect on apple brown spot than the control agent. Therefore, 48% Pyraclostrobin • Tebuconazole SC can be used for the prevention and treatment of apple brown spot disease and the recommended concentration is 3000 times to 5000 times.
Explore More

